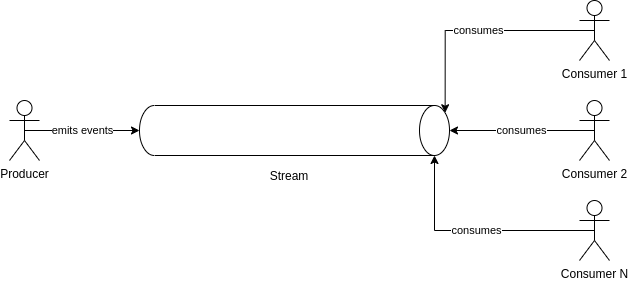
Events¶
UCloud supports event streams, an event stream provides a message pipe. Producers send messages into the pipe and
consumers read and process the messages. We support two types of event streams: EventStreams and
BroadcastingStreams. UCloud implements both types using Redis.
Ordinary Event Streams¶
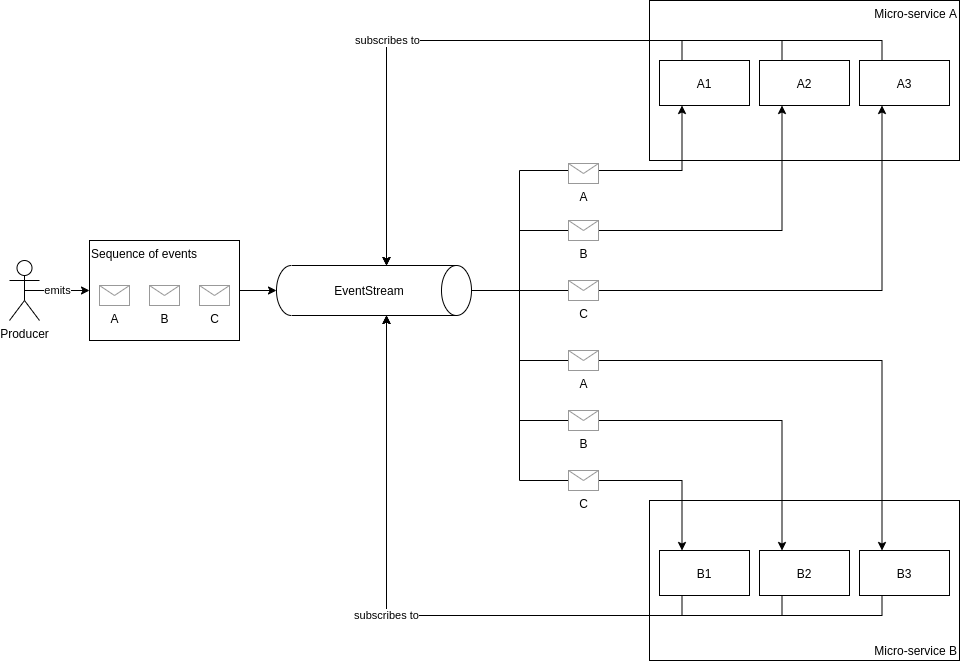
An ordinary EventStream provides a way for services to load-balance events between instances of a given micro-service.
As shown in the figure, the example system contains to micro-services A and B. Both of these micro-services are running
in three instances of the same code. Both micro-services have subscribed to a the same EventStream. When the producer
starts producing messages, those messages are load-balanced across the individual instances of a micro-services. This
means that both service A and service B receives all the messages but the individual messages are load balanced between
the instances of a micro-service.
A consumer does not need to be live when the message is sent for it to be received. Instead, the messages are kept in a persistent list which lives for some time. This list is pruned every once in a while.
Example: Consuming a message
object JobEvents : EventStreamContainer() {
val events = stream<JobEvent>("app-kubernetes-job-events", { it.jobName })
}
suspend fun initializeConsumer() {
micro.eventStreamService.subscribe(JobEvents.events, EventConsumer.Immediate { ev ->
println("received $ev")
})
}
Example: Consuming a batch of messages
suspend fun initializeConsumer() {
micro.eventStreamService.subscribe(
JobEvents.events,
EventConsumer.Batched(maxLatency = 500, maxBatchSize = 1000) { batch ->
println("received $batch")
}
)
}
Example: Producing a message
val eventProducer = micro.eventStreamService.createProducer(ProjectEvents.events)
eventProducer.produce(ProjectEvent.Created("foobar"))
Broadcasting Streams¶
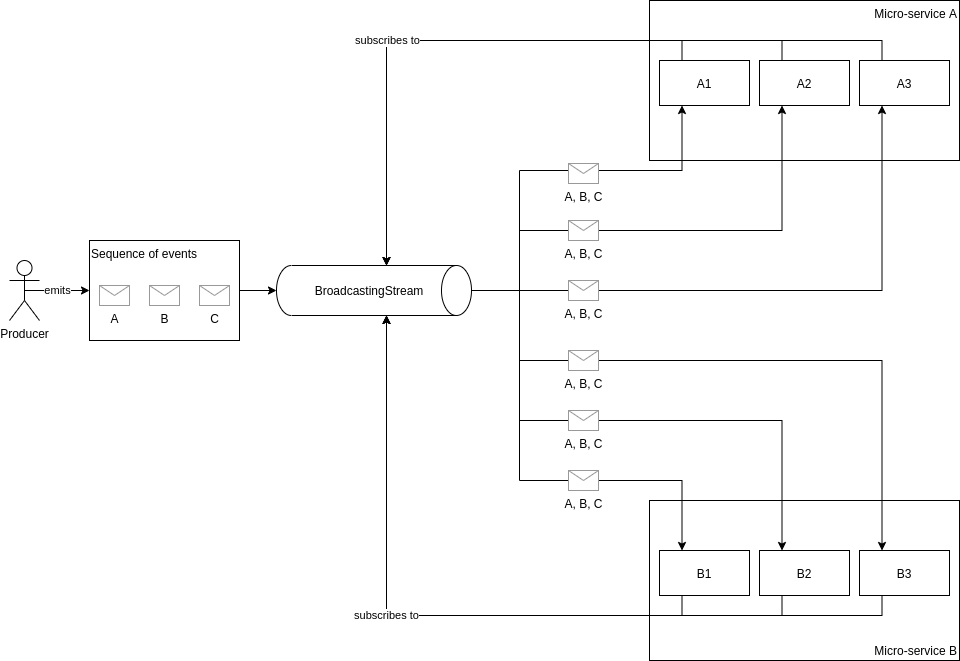
The BroadcastingStream works differently from the EventStream. In this case all consumers receive every message
which is produced.
Only the consumers which are live will receive messages.
Example: Broadcasting a message
val broadcastingStream = RedisBroadcastingStream(micro.redisConnectionManager)
broadcastingStream.broadcast(MyMessage(42), MyStreams.stream)
Example: Subscribing to a stream
broadcastStream.subscribe(CancelWSStream.events) { (id) ->
streams.remove(id)?.close()
}