High-Level Architecture¶
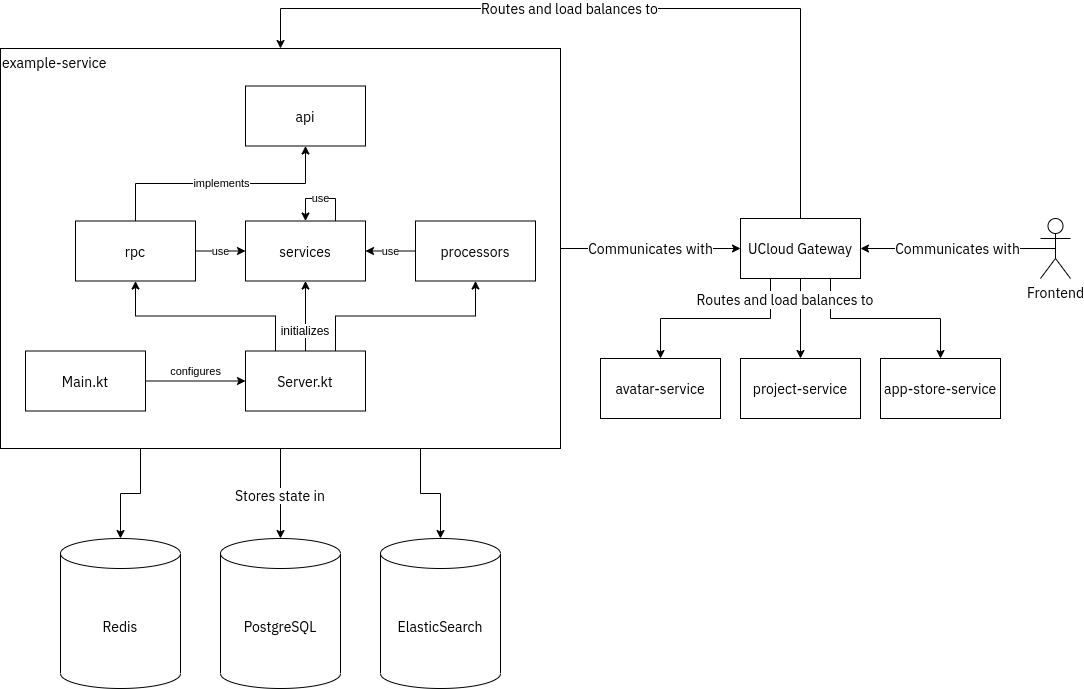
Figure: The overall structure and internals of a generic UCloud service.
Components of a service¶
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
api |
Contains data models and interface descriptions (CallDescriptionContainer). Other services consume these to perform remote procedure calls. |
rpc |
Implements the interfaces provided by api. Delegates work to the services component. |
services |
Implements the business logic of a service. Services in this component can depend on other services and make remote procedure calls to other services. |
processors |
Consumes and processes events from the event stream. |
Main.kt |
Read configuration and initialize Server.kt. |
Server.kt |
Initialize all remaining components. |
Databases¶
UCloud stores state in a number of different general-purpose databases. We use the following databases for general-purpose data:
| Database | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Redis | Event streams and distributed locking mechanism. |
| PostgreSQL | General purpose data storage. |
| ElasticSearch | Storage of state which requires indexing of text. |
For the most part we recommend that you store state in PostgreSQL. Only if the data has a need to be indexed in a
special way should you use ElasticSearch. Redis is used to broadcast and load-balance messages among
services. Redis can also be used to perform distributed locking, for example, to ensure that only a single
service instance is performing a certain task.
UCloud also stores state in other specialized ‘databases’. Examples include a filesystem (we support optimizations for CephFS) and Kubernetes.
Main.kt and Server.kt¶
Main.kt provides an entry point to the service. In this file you should do the following:
Create an
objectwhich implements theServiceinterfaceThe
Serviceinterface is used to register with theLaunchermodule, used to run UCloud in development and in integration testsYou can configure the
Microinstance for additional functionality, such asElasticSearchYou should parse the configuration in the
initializeServerand pass it to `Server.kt
Server.kt receives the configuration from Main.kt and initializes the server:
Initialize components from the
services,processorsandcontrollerscomponentPass
Controllers toconfigureControllers
UCloud Gateway¶
The UCloud gateway is responsible for routing and load balancing to the different services and ther instances. In production, NGINX acts as the gateway.
In development and when using integration testing, the gateway is replaced by a single JVM instance which runs all of
UCloud. The launcher module and the integration-testing module implements this. These modules both
use the Service instances stored in Main.kt to configure routing.
Networking and RPC¶
UCloud has an internal library for exposing type-safe interfaces which can be used for RPC. You can read more about the interfaces here. The type-safe interfaces are used by both the client and server component of UCloud. This significantly reduces the amount of duplicate code required.
Event Streams¶
UCloud provide event streams to allow services communication with other services without knowing the concrete recipients of the code. This allows for loose-coupling of the services. This is particularly useful if a service needs to advertise changes to the core data-model.